Understanding the Role of an Oncology Doctor in Modern Healthcare
In the realm of healthcare, the role of an oncology doctor is pivotal in the fight against cancer. As the prevalence of cancer diagnoses continues to rise globally, understanding the complexity of oncology and the expertise of those who practice in this field is essential for patients and their families who are navigating the challenges of cancer care. This comprehensive article dives deep into the responsibilities, skills, and technologies employed by oncology doctors, demonstrating their commitment to improving patient outcomes.
What is an Oncology Doctor?
An oncology doctor, also known as an oncologist, is a medical professional who specializes in the diagnosis, treatment, and management of cancer. This diverse field of medicine encompasses several subspecialties, including:
- Medical Oncology: Focuses on the treatment of cancer using medications such as chemotherapy, immunotherapy, and targeted therapy.
- Surgical Oncology: Involves the surgical removal of tumors and surrounding tissues to achieve cancer-free margins.
- Radiation Oncology: Utilizes high-energy radiation to shrink tumors and eliminate cancer cells.
- Pediatric Oncology: Deals specifically with cancer in children and adolescents.
The Education and Training Pathway for Oncology Doctors
Becoming an oncology doctor requires extensive education and training. This journey typically involves the following steps:
- Bachelor’s Degree: A four-year undergraduate degree, often in the sciences, serves as the foundation.
- Medical School: An additional four years in medical school to earn either a Doctor of Medicine (MD) or Doctor of Osteopathic Medicine (DO) degree.
- Residency Program: Following medical school, doctors complete a residency in internal medicine, which usually lasts three years.
- Fellowship Training: After residency, aspiring oncologists undergo 2-3 years of specialized fellowship training in oncology.
Upon completion of their training, oncologists often pursue board certification, demonstrating their expertise in the field. Continuing education is also a vital part of their career, ensuring that they remain current with advancements in cancer treatment and research.
The Vital Responsibilities of an Oncology Doctor
The responsibilities of an oncology doctor are multifaceted and crucial in managing a patient's journey through cancer care:
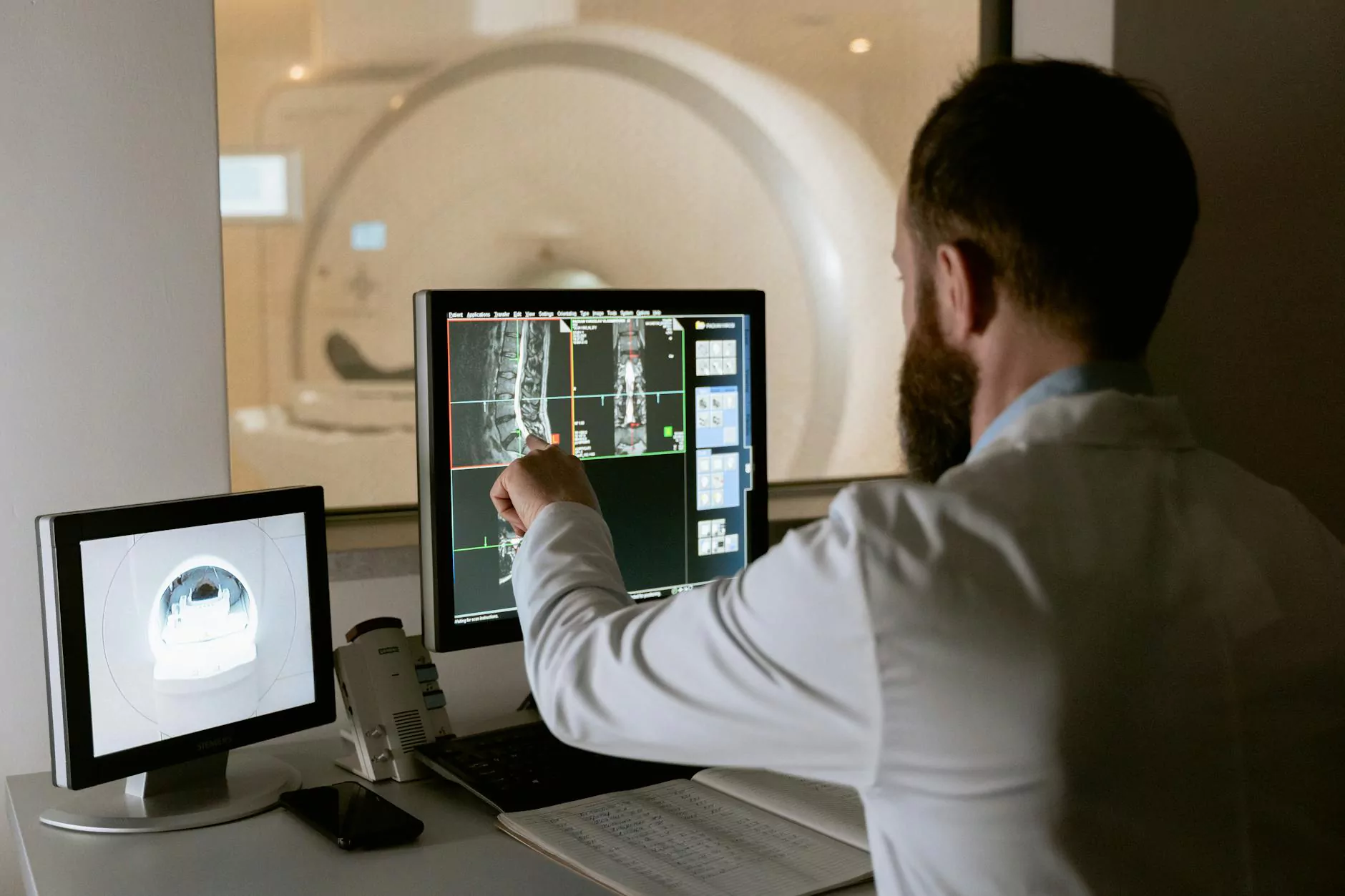
- Diagnosis: Oncology doctors utilize imaging technologies (such as CT scans, MRIs, and PET scans) and various diagnostic tests (like biopsies) to accurately diagnose different types of cancer.
- Treatment Planning: They devise personalized treatment plans based on the type and stage of cancer, considering factors such as the patient’s overall health, preferences, and the latest treatment protocols.
- Patient Education: Oncologists educate patients and their families about the disease, treatment options, potential side effects, and the importance of follow-up care.
- Multidisciplinary Coordination: An effective oncology doctor collaborates with a team of specialists, including surgeons, radiologists, pathologists, and palliative care providers, to coordinate comprehensive cancer care.
- Follow-Up Care: They monitor the effectiveness of treatments and make necessary adjustments, managing any side effects that arise throughout the treatment process.
The Impact of Technology in Oncology
Technology plays a transformative role in the field of oncology, enhancing diagnosis and treatment options. Some key advancements include:
Precision Medicine
Precision medicine allows oncology doctors to tailor treatments based on the genetic makeup of both the patient and the tumor. This approach increases the effectiveness of treatments by targeting specific cancer cell characteristics.
Immunotherapy
Recent advancements in immunotherapy have changed the landscape of cancer treatment. Oncology doctors are now able to harness the body's immune system to fight cancer more effectively, offering hope for patients with previously hard-to-treat cancers.
Telemedicine
In response to the evolving healthcare landscape, many oncology practices have integrated telemedicine. This innovation allows patients to consult with their oncology doctor remotely, making cancer care more accessible without compromising quality.
Challenges Faced by Oncology Doctors
While the role of an oncology doctor is incredibly rewarding, it is not without challenges:
- Emotional Burden: Regularly dealing with life-threatening illnesses can take a toll on the emotional well-being of oncology doctors.
- Patient Prognosis: Delivering unfavorable news about prognosis is a challenging part of the job, requiring compassion and sensitivity.
- Keeping Up with Research: The rapid pace of innovation and research in cancer treatment demands ongoing education and adaptability.
Patient-Centered Care in Oncology
For an oncology doctor, patient-centered care means prioritizing the needs and preferences of patients throughout their treatment journey. This encompasses:
- Empathy: Understanding the patient's emotional and psychological needs.
- Communication: Maintaining open lines of communication about treatment plans, side effects, and lifestyle adjustments.
- Holistic Considerations: Acknowledging the importance of physical, emotional, and social well-being in the overall treatment strategy.
The Future of Oncology
The field of oncology is evolving, with several exciting trends on the horizon:
Artificial Intelligence and Oncology
With the rise of artificial intelligence, oncology doctors are beginning to use AI-driven tools to enhance diagnostic accuracy, analyze large volumes of patient data, and predict treatment outcomes, leading to more informed decision-making.
Advancements in Targeted Therapies
The future will likely see even more refined targeted therapies that can better distinguish between cancerous and healthy cells, leading to fewer side effects and more effective treatment modalities.
Collaborative Research Efforts
As cancer research becomes increasingly collaborative, oncologists will benefit from sharing insights and findings across institutions, leading to a faster translation of research into clinical practice.
Conclusion
The role of an oncology doctor is indispensable in today's healthcare landscape. With their comprehensive education, specialized skills, and deep commitment to patient care, oncology doctors are at the forefront of cancer management. Their unwavering dedication to evolving treatments, combined with technological advancements, promises to enhance the future of oncology, providing hope and improved outcomes for countless patients battling cancer. Understanding the multifaceted role of these specialists not only demystifies the oncology field but also empowers patients and their families to engage more fully in their care journey.